CRISPR-U™ Gene Knockout Cell Line
Strategy
CAV1 Gene Knockout Strategy
CRISPR-U™ technology (CRISPR based), developed by Ubigene, is more efficient than general
CRISPR/Cas9 technology in double-strand breaking and homologous recombination. With CRISPR-U™, Ubigene has
successfully edited over 3000 genes on more than 100 types of cell lines.
Objective
To create a Human CAV1 Knockout
model in cell line by
CRISPR-U™-mediated
genome
engineering.
Target gene info 
| Official symbol | CAV1 |
| Gene id | 857 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Official full symbol | caveolin 1 |
| Gene type | protein-coding |
| Also known as | BSCL3, CGL3, LCCNS, MSTP085, PPH3, VIP21 |
| Summary | The scaffolding protein encoded by this gene is the main component of the caveolae plasma membranes found in most cell types. The protein links integrin subunits to the tyrosine kinase FYN, an initiating step in coupling integrins to the Ras-ERK pathway and promoting cell cycle progression. The gene is a tumor suppressor gene candidate and a negative regulator of the Ras-p42/44 mitogen-activated kinase cascade. Caveolin 1 and caveolin 2 are located next to each other on chromosome 7 and express colocalizing proteins that form a stable hetero-oligomeric complex. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy. Alternatively spliced transcripts encode alpha and beta isoforms of caveolin 1. |
| Genomic regions | Chromosome 7 |
Strategy Summary
This gene has 7 protein coding transcripts:
| Name | Transcript ID | bp | Protein | Biotype | CCDS | UniProt Match | RefSeq Match | Flags |
| CAV1-205 | ENST00000405348.6 | 2652 | 147aa | Protein coding | CCDS55156 | Q03135-2 | - | TSL:5, GENCODE basic, APPRIS ALT1, |
| CAV1-202 | ENST00000393467.1 | 2628 | 147aa | Protein coding | CCDS55156 | Q03135-2 | - | TSL:1, GENCODE basic, APPRIS ALT1, |
| CAV1-201 | ENST00000341049.7 | 2456 | 178aa | Protein coding | CCDS5767 | Q03135-1 | NM_001753.5 | TSL:1, GENCODE basic, APPRIS P3, MANE Select v0.92, |
| CAV1-203 | ENST00000393468.1 | 845 | 147aa | Protein coding | CCDS55156 | Q03135-2 | - | TSL:1, GENCODE basic, APPRIS ALT1, |
| CAV1-209 | ENST00000614113.5 | 1130 | 115aa | Protein coding | - | Q03135-2 | - | TSL:1, GENCODE basic, |
| CAV1-204 | ENST00000393470.1 | 598 | 167aa | Protein coding | - | E9PCT5 | - | TSL:4, GENCODE basic, |
| CAV1-207 | ENST00000456473.5 | 557 | 138aa | Protein coding | - | C9JKI3 | - | CDS 3' incomplete, TSL:4, |
| CAV1-206 | ENST00000451122.5 | 1653 | 86aa | Nonsense mediated decay | - | F8WDM7 | - | TSL:1, |
| CAV1-208 | ENST00000489856.1 | 575 | No protein | Retained intron | - | - | - | TSL:2, |




Red Cotton™ Assessment
Project Difficulty Level unknown
| Target Gene | CAV1 |
| This KO Strategy | loading |
| Red Cotton™ Notes | Gene CAV1 had been KO in hela cell line. |
Aforementioned information comes from Ubigene database. Different origin of cell lines may have
different condition. Ubigene reserved all the right for final explanation.
Special deals for this gene:
$49
Single gRNA plasmid off-shelf
$599
Single gRNA lentivirus



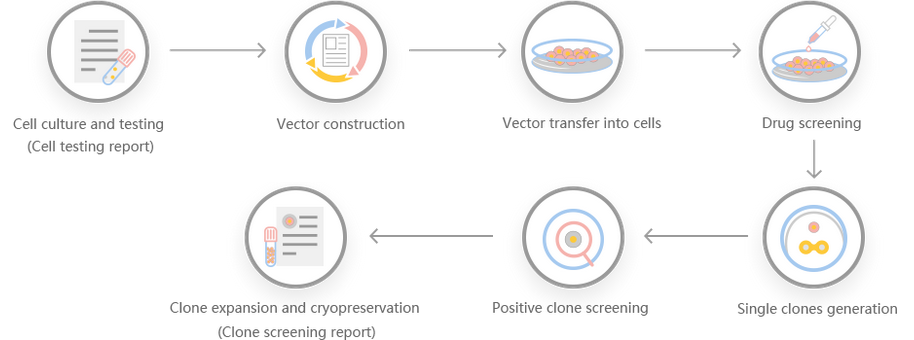
Work flow





 Comment:
Comment: