CRISPR-U™ Gene Knockout Cell Line
Strategy
KCNQ3 Gene Knockout Strategy
CRISPR-U™ technology (CRISPR based), developed by Ubigene, is more efficient than general
CRISPR/Cas9 technology in double-strand breaking and homologous recombination. With CRISPR-U™, Ubigene has
successfully edited over 3000 genes on more than 100 types of cell lines.
Objective
To create a Human KCNQ3 Knockout
model in cell line by
CRISPR-U™-mediated
genome
engineering.
Target gene info 
| Official symbol | KCNQ3 |
| Gene id | 3786 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens |
| Official full symbol | potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily Q member 3 |
| Gene type | protein-coding |
| Also known as | BFNC2, EBN2, KV7.3 |
| Summary | This gene encodes a protein that functions in the regulation of neuronal excitability. The encoded protein forms an M-channel by associating with the products of the related KCNQ2 or KCNQ5 genes, which both encode integral membrane proteins. M-channel currents are inhibited by M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and are activated by retigabine, a novel anti-convulsant drug. Defects in this gene are a cause of benign familial neonatal convulsions type 2 (BFNC2), also known as epilepsy, benign neonatal type 2 (EBN2). Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. |
| Genomic regions | Chromosome 8 |
Strategy Summary
This gene has 5 protein coding transcripts:
| Name | Transcript ID | bp | Protein | Biotype | CCDS | UniProt Match | RefSeq Match | Flags |
| KCNQ3-201 | ENST00000388996.10 | 11583 | 872aa | Protein coding | CCDS34943 | O43525-1 | NM_004519.4 | TSL:1, GENCODE basic, APPRIS P2, MANE Select v0.92, |
| KCNQ3-204 | ENST00000521134.6 | 2577 | 752aa | Protein coding | CCDS56554 | O43525-2 | - | TSL:2, GENCODE basic, APPRIS ALT2, |
| KCNQ3-205 | ENST00000621976.1 | 10659 | 751aa | Protein coding | - | A0A087WZB4 | - | TSL:5, GENCODE basic, |
| KCNQ3-202 | ENST00000519445.5 | 2801 | 860aa | Protein coding | - | E7ET42 | - | TSL:5, GENCODE basic, APPRIS ALT2, |
| KCNQ3-206 | ENST00000638588.1 | 2190 | 716aa | Protein coding | - | A0A1W2PQ71 | - | CDS 3' incomplete, TSL:5, |
| KCNQ3-208 | ENST00000639496.1 | 4943 | 319aa | Nonsense mediated decay | - | A0A1W2PNZ2 | - | TSL:5, |
| KCNQ3-207 | ENST00000639358.1 | 822 | 89aa | Nonsense mediated decay | - | A0A1W2PRN8 | - | CDS 5' incomplete, TSL:5, |
| KCNQ3-203 | ENST00000519589.1 | 3464 | No protein | Retained intron | - | - | - | TSL:2, |




Strategy
Click to get 
Red Cotton™ Assessment
Project Difficulty Level unknown
| Target Gene | KCNQ3 |
| This KO Strategy | loading |
| Red Cotton™ Notes | Gene KCNQ3 had been KO in a549 cell line. |
Aforementioned information comes from Ubigene database. Different origin of cell lines may have
different condition. Ubigene reserved all the right for final explanation.
Special deals for this gene:
$49
Single gRNA plasmid off-shelf
$599
Single gRNA lentivirus



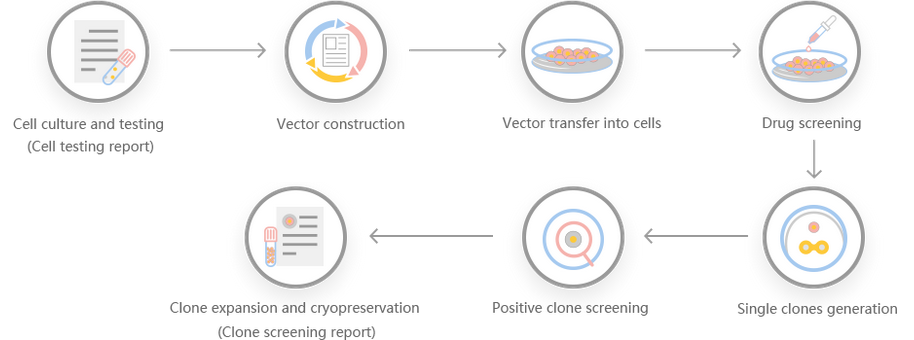
Work flow




 Comment:
Comment: